All-in-One PCs for Gaming: Worth It or Not?
These sleek systems handle casual games fine but struggle with modern titles due to heat and weak graphics. Learn what to expect before you buy.
Build, upgrade, and troubleshoot with clear hardware-focused guides.
Computer hardware is everything you can physically touch inside your PC. Each part has a specific job: the processor runs calculations, the graphics card renders what you see on screen, memory holds whatever you're actively working on, and storage drives keep your files when the power is off. The motherboard ties it all together, the power supply keeps it running, and cooling systems stop it from overheating. Understanding how these parts work helps you build, upgrade, and troubleshoot with confidence.
Spec sheets can be overwhelming if you don't know what to look for. Processors advertise core counts and clock speeds, graphics cards highlight memory amounts, and RAM sticks list speeds and timings. Most of these numbers only matter in context. Our guides explain which specs actually affect real-world performance so you can compare parts meaningfully instead of chasing the biggest number on the box.
View buying guides
View cases guides
View cooling guides
View cpu guides
View gpu guides
View laptops guides
View maintenance guides
View motherboards guides
View power guides
View ram guides
View storage guides
View troubleshooting guides

These sleek systems handle casual games fine but struggle with modern titles due to heat and weak graphics. Learn what to expect before you buy.

Match your CPU socket to the motherboard, verify RAM type, check power supply wattage, and confirm your graphics card fits in the case.

Don't get scammed. Check the battery, test all ports, run diagnostics, verify the specs match the listing, and confirm Windows is legit.

Expect 5-8 years of use with proper care, though high-end systems can reach 10 years. Learn which parts fail first and how to extend your PC's life.

Check CPU cores, graphics card, and RAM. Budget PCs have 2-4 cores and 8GB RAM while gaming systems have 8+ cores and 32GB+ RAM.

Mid towers fit most builds, cost less, and save space. Full towers are for oversized boards, lots of drives, or custom cooling.

PCs can sit on carpet but risk overheating, dust buildup, and static damage. Use a stand or platform for proper airflow and protection.

Fan curves tell your PC fans when to speed up or slow down based on temperature. Set them up in BIOS or with free software for quieter cooling.

Set up 2-3 intake fans in front and 1-2 exhaust fans at the rear and top. Keep intake CFM 10-20% higher than exhaust for balanced cooling and less dust.

Clean dust from fans, replace thermal paste, and improve case airflow to fix an overheating gaming PC. These steps stop crashes and protect your parts.

Your CPU or GPU automatically slows down to prevent overheating. Learn why it happens, how to detect it, and proven fixes to restore full performance.

Running at 100% is normal for brief tasks. Prolonged high usage only causes problems if your cooling system can't control the heat it creates.

A processor with heat damage shows crashes, slowdowns, throttling, and boot failures. Monitor temps and run stress tests to confirm the damage.

CPUs generate heat as transistors switch, turning power into thermal energy. See typical wattage and normal temperature ranges.

LGA has pins on the motherboard, PGA puts them on the CPU, and BGA is soldered permanently. Know the difference before upgrading your processor.

The CPU is your computer's brain that handles every click, app, and game. Learn how processors work and what makes some faster than others.

Intel CPUs use LGA sockets where pins live in the motherboard, not the chip. This protects your processor from bent pin damage during handling.

Confirm your CPU works by checking boot behavior, Task Manager usage, and HWMonitor temps, plus quick tests for stability.

Not always. Integrated graphics work fine for web browsing and office tasks, but you need a dedicated GPU for gaming, video editing, or 3D work.

Most GPUs overheat from dust buildup, poor case airflow, or old thermal paste. Safe gaming temps are 149-181F. Learn how to diagnose and fix the problem.

GPU scalping is buying graphics cards in bulk with bots, then reselling at 2-3x the retail price. Learn how scalpers operate and how to avoid them.

Remove your graphics card cooler, clean old paste with thermal remover, apply fresh compound, and reassemble. Expect 18-36°F (10-20°C) cooler temps.

Use MSI Afterburner to control your GPU fans. Set 60-70% for cooler temps, or create custom curves that adjust speed based on temperature.

A graphics card contains a GPU chip, video memory, cooling system, power delivery, and display ports that work together to create images on your screen.

Test your graphics card using Task Manager and MSI Afterburner. Healthy GPUs run 140-185°F (60-85°C) under load with no visual artifacts or crashes.

Low GPU usage usually means your CPU can't keep up, VSync is capping frames, or drivers need updating. Here's how to fix it and boost performance.

Graphics cards have dedicated VRAM to store textures and frames near the GPU, providing 10 to 18 times faster access than system RAM.

Look for a keyboard icon with light rays on your F5 to F10 keys, then press Fn plus that key. If the keys light up, you have a backlit keyboard.

When a laptop battery dies, it shuts down and you can lose unsaved work. See what happens next and how to protect battery life.

Fans may cycle every 10-15 minutes in light use and spin up around 140-158 F. Constant idle fan noise can signal cooling issues.

Cool down an overheating laptop with one Windows setting. Lower CPU to 75%, clean vents, and use these 8 methods to keep it running cool.

Skip it. MacBook screen protectors can damage the anti-reflective coating and even crack the display due to tight lid clearance.

Laptop batteries lose 20% capacity after 300-500 charge cycles due to lithium-ion chemistry limits, heat buildup, and chemical aging inside the cells.

MacBooks have USB ports, just not USB-A. Apple uses USB-C for 8x faster speeds, 100W charging, and thinner designs. Adapters work with all old devices.

Use positive air pressure with filtered intake fans, keep your PC off the floor, and clean filters monthly. These steps block most dust from entering.

Lay your PC flat on the back seat with padding, remove the graphics card and hard drives first, and secure everything with seat belts to prevent damage.

Keep your PC running fast with weekly disk cleanup, monthly updates, regular virus scans, and dust removal every few months. Simple steps anyone can do.

Keep it sealed at 59-77°F (15-25°C) with humidity below 50%. Metal types last 3-5 years, ceramic 2-3 years, and carbon types 3-4 years unopened.

Every 2-5 years for office PCs, 2-3 years for gaming, and 1-2 years for overclocked systems. Replace sooner if temps rise 18°F (10°C) above normal.

The CR2032 coin cell powers a chip that saves your BIOS settings and keeps the clock running when the computer is off.

PS/2 ports provide guaranteed BIOS access, zero polling latency, and work when USB fails. Essential for IT pros, gamers, and secure environments.

Gaming PCs use 300-800 watts during play sessions, costing $10-25 monthly. See the full breakdown by component and tips to lower your electric bill.

A PSU converts wall outlet electricity into the voltages your PC needs. Learn about wattage, efficiency ratings, modularity, and protection features.

A quality PSU lasts 5-10 years, while budget units may fail in 3-5 years. Discover failure warning signs and proven ways to extend your unit's lifespan.

Four RAM sticks are not slower than two when using the same total amount and speed. Performance depends on your motherboard quality.

Use a pencil eraser to gently rub dirt and oxidation off the gold pins, wipe with a lint-free cloth, and blow away debris with compressed air.

Most people need 16GB of RAM for everyday use and gaming. 8GB handles basic tasks, while 32GB or more suits video editing, 3D work, and heavy multitasking.

Learn why RAM always comes in powers of 2. Binary addressing doubles capacity per bit, leading to standard sizes like 4GB, 8GB, 16GB, and 32GB.

Yes, solid state drives develop bad sectors as memory cells wear out. Your drive automatically replaces failed cells with spare blocks.

Internal drives are faster for apps and games. External drives are portable for backups. See which fits your storage needs and budget.

SSDs lose 40-50% write speed above 75% capacity because flash memory cannot overwrite data directly and must erase entire blocks first.

Both positions work safely for HDD storage. Horizontal mounting offers better stability and airflow, but modern drives perform equally either way.

Yes, old hard drives work with new motherboards. Expect driver conflicts and Windows issues. SATA connects directly, IDE needs an adapter.
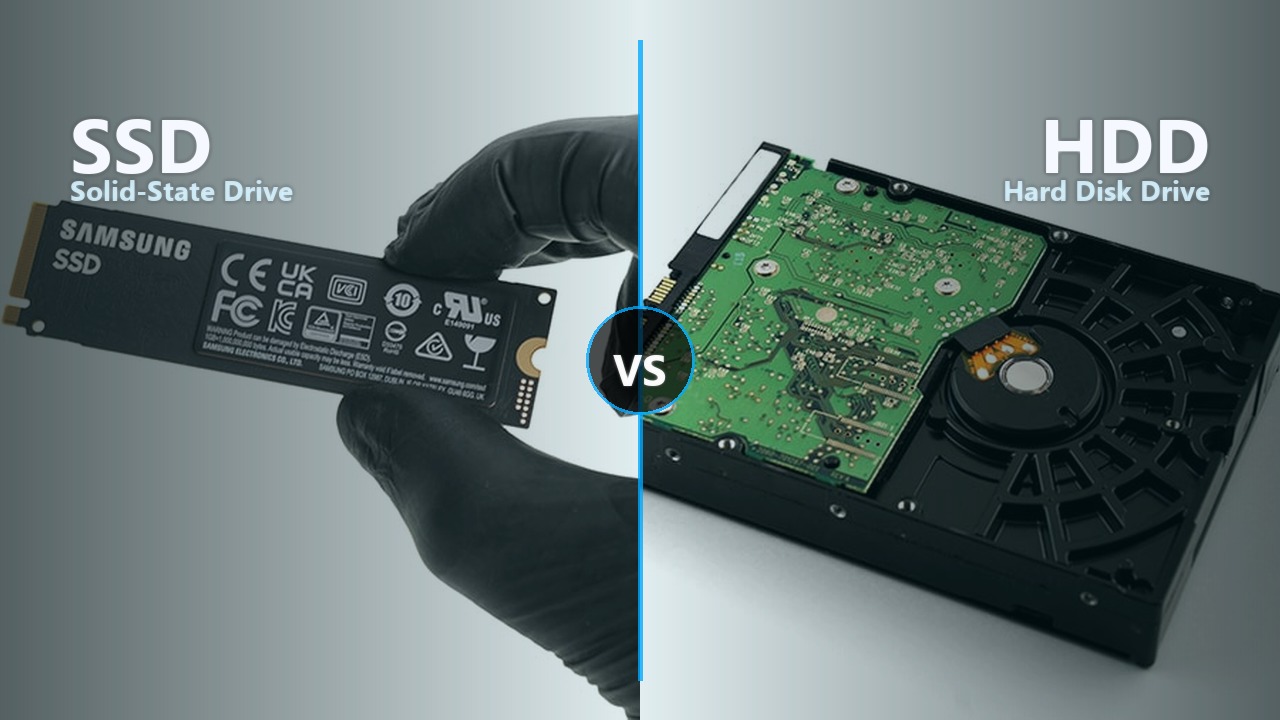
SSDs are 5-20x faster with no moving parts. HDDs store more data for less money. Compare speed, price, durability, and noise to pick the right drive.

Diagnose processor vs motherboard failures with systematic testing. Check power, test CPU stress, examine connections for accurate diagnosis.

No, BSOD crashes won't damage your PC. They protect your hardware by shutting down Windows before real damage from overheating or failing RAM occurs.

Press the power button on the front of your computer case. First check that all cables are connected and the PSU switch is set to ON.

Computers slow down due to software bloat, full storage drives, and hardware wear. Most slowdowns are fixable with cleanup and simple upgrades.