PC airflow optimization is essential for maintaining optimal cooling performance and extending hardware component lifespan. Poor case airflow causes thermal throttling, reduces hardware longevity, and increases fan noise levels. Effective PC airflow optimization involves strategic cooling fan placement, balanced air pressure management, and regular system maintenance to keep your computer running cool and quiet.
It's because forced airflow from fans completely overrides natural convection. In your room, hot air rises slowly because it's less dense, that's natural convection at work. But inside your PC, fans create forced convection that's hundreds of times stronger than natural air movement. A single 120mm fan moving at 1000 RPM generates enough airflow to completely dominate any natural rising tendency. This is why you can mount exhaust fans at the bottom of a case and they'll still work perfectly, the fan's pressure overcomes gravity's effect on hot air. It's also why a PC with no fans will overheat even with vents at the top, because natural convection is far too weak to cool modern components generating 200+ watts of heat. The lesson? Fan placement and direction matter way more than relying on "hot air rises." Your case needs active airflow management, not passive hope.
PC airflow optimization creates balanced air pressure where cool ambient air enters through filtered intake vents, flows efficiently over internal components, and exits through exhaust fans. Maintain slightly positive air pressure (10-20% more intake CFM than exhaust CFM) for optimal thermal cooling and dust control.
Through years of testing different airflow configurations and cooling setups, I've found the temperature difference between optimized and poor cooling setups can be 10-15 C in component temperatures. This airflow guide covers proven optimization techniques and real-world testing methods to help you achieve optimal PC case cooling performance.
Understanding PC Case Airflow Fundamentals
Think of your PC case as a wind tunnel where hot exhaust air needs to escape and cool fresh air needs to reach your internal components. When case airflow is restricted or poorly designed, hot air gets trapped around your CPU processor and GPU graphics card, forcing them to throttle performance.
Signs Your PC Airflow Needs Optimization
- High component temperatures during light usage (CPU >70 C, GPU >80 C at idle)
- Cooling fans constantly ramping up or running at maximum fan speed
- Dust accumulation in unfiltered case areas within weeks
- Hot temperature spots near GPU, CPU, or power supply unit components
- System crashes or thermal throttling during gaming sessions
- Temperature differences >15 C between case top and bottom areas
PC Case Pressure Types and Optimization
Understanding air pressure dynamics is crucial for effective airflow optimization. Each pressure configuration affects cooling performance and dust control differently.
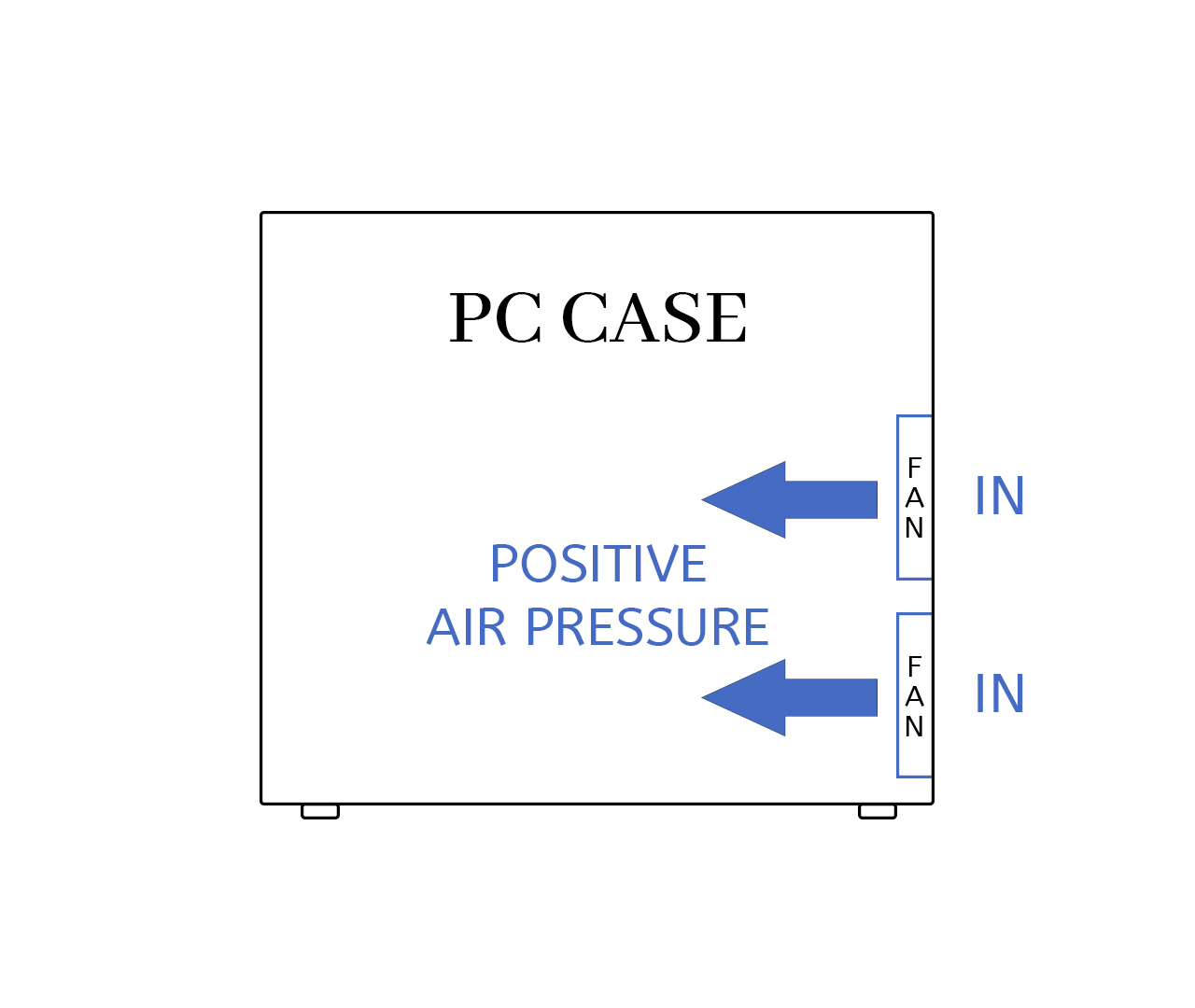
Positive Air Pressure Configuration (Recommended)
More intake fan CFM than exhaust fan CFM creates positive case pressure. Air pushes out through every case gap, preventing dust from entering unfiltered openings. This pressure configuration works best for most gaming PC builds and workstation systems.
Optimal for: Gaming PCs, workstation builds, dusty room environments
- Superior dust control through filtered intake fans
- Consistent component cooling across all hardware
- Easier system maintenance and filter cleaning
- Predictable airflow patterns throughout case
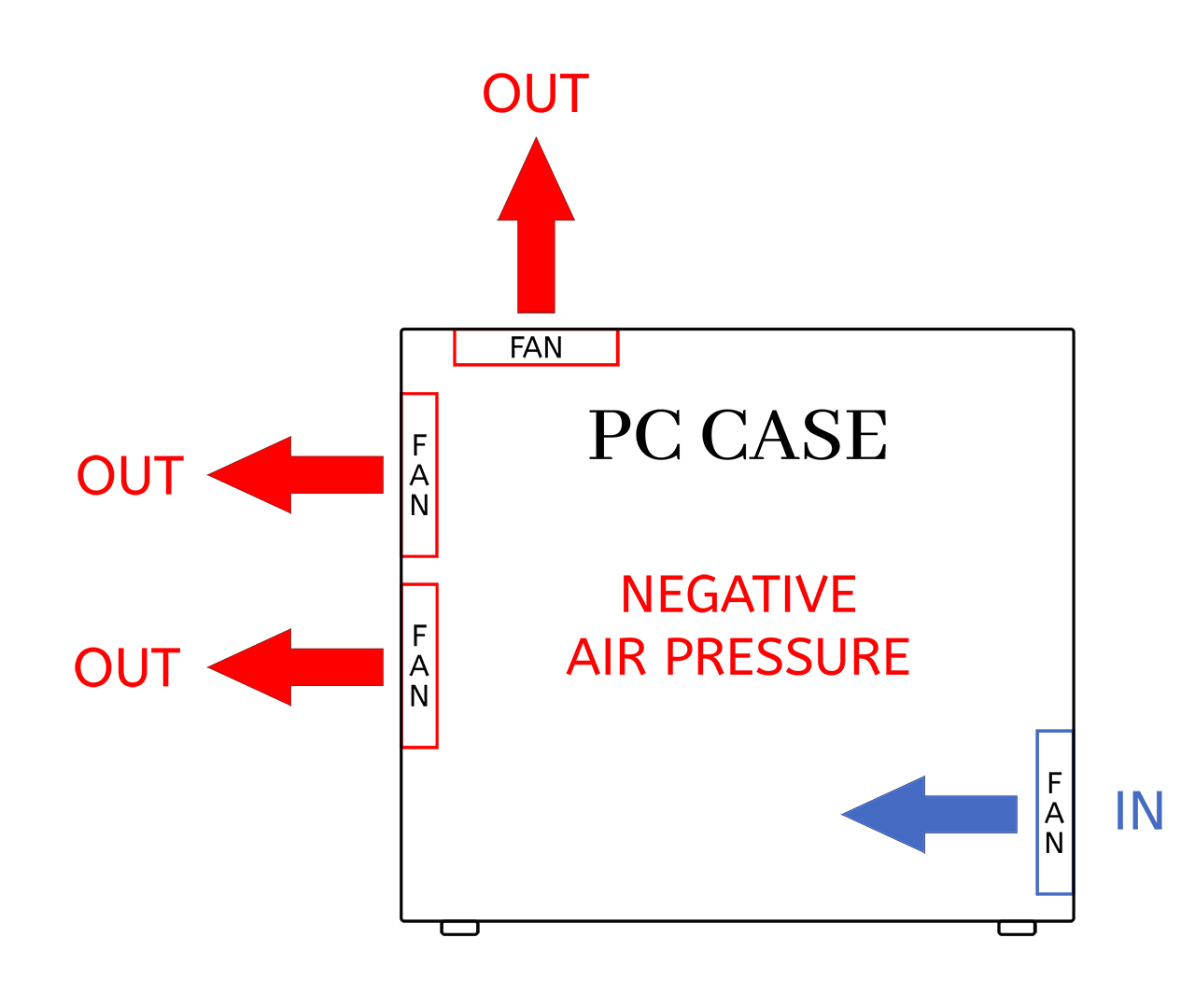
Negative Air Pressure Configuration
More exhaust fan CFM than intake fan CFM creates vacuum pressure effect. Air gets pulled in through every case opening, potentially bringing dust through unfiltered gaps but excelling at hot exhaust air removal.
Optimal for: High-performance PC builds, cases with excellent dust filtration
- Efficient hot air extraction from case
- Helps cool hard-to-reach PC components
- Better cooling performance under extreme workloads
- Requires more frequent dust filter cleaning
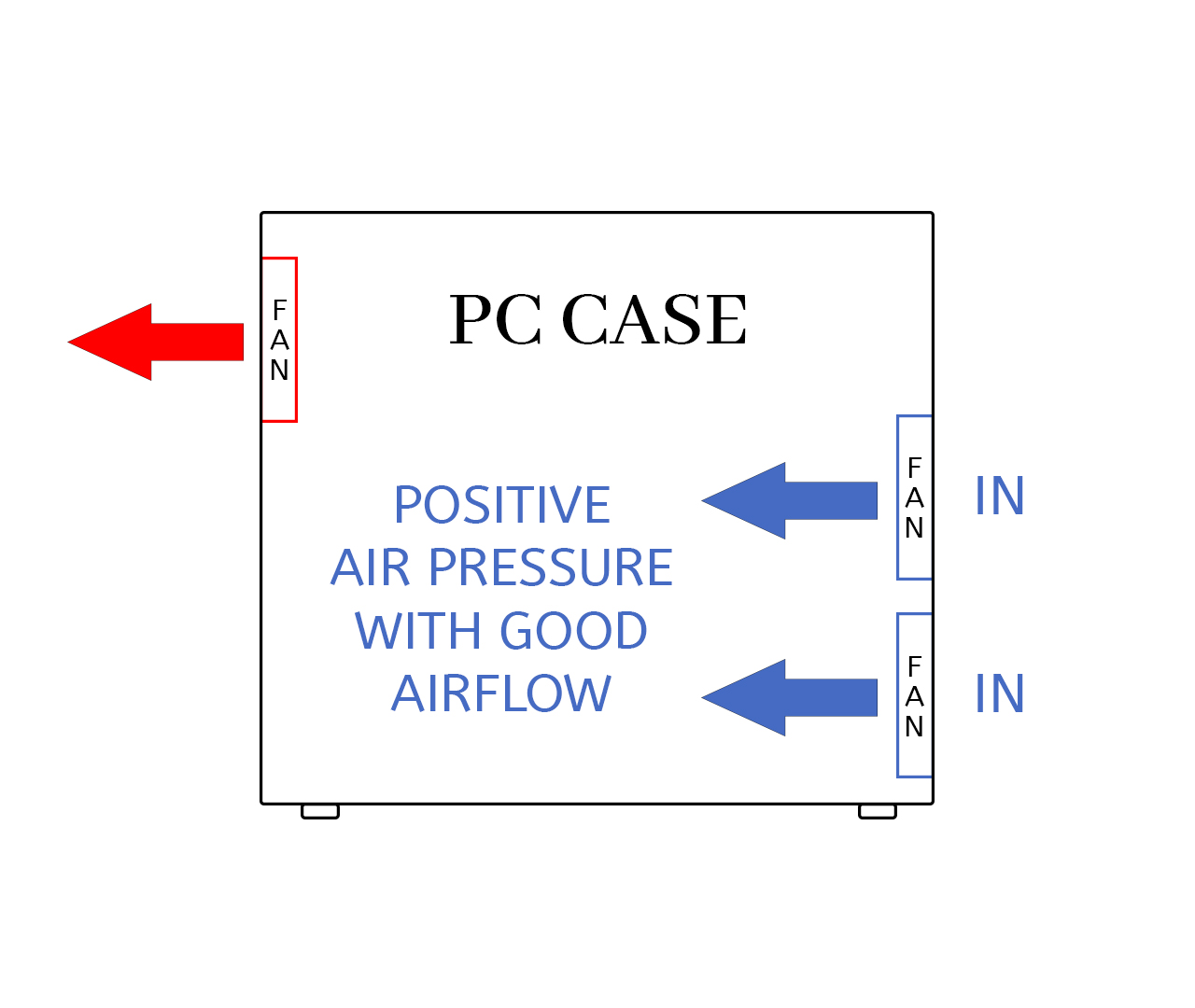
Balanced Air Pressure Configuration (The Sweet Spot)
Slightly more intake airflow than exhaust airflow (10-20% CFM difference) provides positive pressure benefits while maintaining excellent cooling performance. This represents the optimal airflow balance for most PC builds.
Optimal for: Most gaming and workstation PC builds
- Combines effective dust control with efficient component cooling
- Predictable and stable airflow movement patterns
- Optimal pressure balance for most use cases
- Easy to maintain and adjust fan speeds
Optimal PC Case Fan Configuration Strategies
These proven fan configurations work well in most PC cases. Use them as starting points and adjust based on your specific case setup and hardware component requirements.
Basic Fan Setup (2-3 Case Fans)
- Minimum Configuration: One 120mm front intake fan + one 120mm rear exhaust fan
- Improved Setup: Two front intake fans + one rear exhaust fan for positive air pressure
- CFM Target: 10-20% more intake fan CFM than exhaust fan CFM
Mid-Tower Gaming PC Configuration
- Front Panel: Two 140mm intake fans (with dust filters)
- Rear Panel: One 120mm exhaust fan
- Top Panel: One 120mm exhaust fan (optional configuration)
- Bottom Panel: One 120mm intake fan for direct GPU cooling (if case supports)
High-Performance PC Configuration
- Front Panel: Three 120mm or two 140mm intake fans
- Top Panel: Two 140mm exhaust fans or AIO liquid cooling radiator
- Rear Panel: One 120mm exhaust fan
- Side/Bottom Panel: Additional intake fans for GPU graphics card if case supports
PC Airflow Optimization Techniques
These airflow optimization methods can improve component temperatures without purchasing additional cooling fans. Focus on maximizing cooling efficiency of your existing fan setup.
No-Cost Airflow Improvements
- Fan Direction Check: Verify all case fans blow in intended directions using fan housing airflow arrows
- Cable Management: Route power cables and data cables behind motherboard tray to clear airflow paths
- Filter Cleaning: Clean dust filters monthly for unrestricted intake airflow
- Case Positioning: Elevate PC case slightly for better bottom panel intake airflow
- Fan Repositioning: Move case fans to create better intake/exhaust CFM balance
Advanced Airflow Optimization Methods
- Fan Curve Tuning: Create custom fan curves balancing noise levels and cooling performance
- Airflow Channeling: Use cardboard or plastic shrouds to direct airflow to specific hot components
- Component Spacing: Ensure adequate clearance around heat-generating hardware components
- Intake Filtering: Add quality dust filters to maintain positive pressure cooling benefits
Component-Specific Airflow Optimization
Different PC components have unique cooling requirements. Optimize case airflow patterns to address each hardware component's specific thermal needs.
GPU Graphics Card Airflow Optimization
- Direct Intake: Position front or bottom intake fans to feed cool ambient air directly to GPU cooler
- Exhaust Path: Ensure clear airflow path for GPU exhaust heat to exit case
- Vertical Clearance: Maintain 2-3 PCIe slot spacing above GPU for proper air circulation
- Side Panel Clearance: Keep 20-30mm clearance from side panel for GPU air circulation
CPU Processor Airflow Optimization
- Air Cooler Direction: Orient CPU tower cooler to match case airflow direction (front to back)
- AIO Radiator Placement: Mount AIO radiators as intake for better CPU cooling, exhaust for better overall case temps
- VRM Cooling: Ensure some case airflow reaches motherboard VRM power delivery heatsinks
- Memory Clearance: Avoid blocking RAM memory airflow with oversized CPU air coolers
Testing and Measuring Airflow Optimization Results
Proper airflow testing helps you verify optimization effectiveness and identify problem areas for improvement.
Temperature Monitoring Methods
- Hardware Monitoring Software: Use HWiNFO64, Core Temp, or MSI Afterburner for component temperature tracking
- Stress Testing: Run Prime95 (CPU stress) and FurMark (GPU stress) to test cooling under load
- Ambient Temperature Comparison: Monitor component temps relative to room ambient temperature
- Long-term Monitoring: Track component temperatures over weeks to identify thermal trends
Physical Airflow Testing Methods
- Tissue Paper Test: Place small tissue pieces near case vents to observe air movement direction
- Temperature Mapping: Use multiple temperature sensor probes to identify hot spots and airflow dead zones
- Fan Speed Analysis: Monitor fan RPM speed changes during different computing workloads
- Dust Pattern Analysis: Observe where dust accumulates to understand actual airflow paths
Safety Warning: Never use smoke or other potentially harmful substances for airflow testing near sensitive electronics. Always ensure proper ventilation and safety precautions.
Common PC Airflow Optimization Mistakes
These frequent airflow mistakes can significantly impact cooling performance. Avoid these common issues to maintain optimal case airflow.
- Excessive Exhaust Fans: Too many exhaust fans create negative air pressure and dust infiltration
- Incorrect Fan Orientation: Always verify fan airflow direction using fan housing arrows before installation
- Blocked Intake Vents: Front case panels or dust filters restricting intake airflow more than 30%
- Fighting Airflow: Case fans working against each other instead of creating unified airflow
- Ignoring Cable Management: Power cables and data cables blocking critical airflow pathways
- Overcrowded Components: Insufficient physical spacing between heat-generating hardware components
- Neglecting Maintenance: Dirty dust filters and dusty fans reducing overall airflow efficiency
Advanced Airflow Optimization Techniques
For PC enthusiasts seeking maximum cooling optimization, these advanced airflow techniques provide detailed thermal analysis and fine-tuning capabilities.
Fan Speed Control and Monitoring
- Custom Fan Curves: Create temperature-based fan speed profiles for different usage scenarios
- Fan Control Software: Use SpeedFan, Fan Control software, or motherboard BIOS utilities
- Automated Fan Profiles: Set different fan speed profiles for idle, gaming, and stress testing scenarios
- Temperature Targets: Set appropriate temperature threshold targets for different PC components
Professional Optimization Methods
- Thermal Imaging: Use thermal imaging cameras to identify component hot spots and airflow dead zones
- Pressure Mapping: Measure air pressure differences at various measurement points in your PC case
- Airflow Velocity Testing: Use anemometer tools to measure actual air movement speeds
- Component Temperature Profiling: Create detailed thermal temperature maps for precision optimization
Real-World Airflow Optimization Results
Based on extensive testing across different PC case types and cooling configurations, here are typical temperature improvements you can expect from proper airflow optimization.
Temperature Improvements by Optimization Level
- Basic Airflow Optimization: 3-7 C temperature improvement in CPU/GPU operating temperatures
- Balanced Pressure Setup: 5-10 C thermal improvement with better dust control
- Advanced Configuration: 8-15 C temperature improvement in high-performance gaming builds
- Custom Fan Curves: Additional 2-5 C cooling improvement with noise level reduction
Performance Impact
- Thermal Throttling Reduction: 15-25% performance improvement in thermally limited computing scenarios
- Component Longevity: Significantly extended hardware lifespan for CPUs, GPUs, and other heat-sensitive components
- System Stability: Reduced system crashes and unexpected shutdowns during intensive computing tasks
- Noise Levels: 10-20dB fan noise reduction with optimized fan speed curves
Maintaining Optimal PC Airflow
Consistent system maintenance ensures your airflow optimization remains effective over extended time.
Regular Airflow Maintenance Schedule
- Monthly: Clean dust filters and check cooling fan operation
- Quarterly: Deep clean PC case interior and verify cable management routing
- Bi-annually: Review fan speed curves and temperature monitoring data
- Annually: Complete airflow assessment and optimization configuration review
Conclusion: Achieving Optimal PC Airflow
Proper PC airflow optimization can dramatically improve your computer system's cooling performance, hardware component longevity, and overall system stability. Start with the basic airflow techniques outlined in this optimization guide, then gradually implement more advanced cooling methods based on your specific needs and hardware component requirements.
Remember that airflow optimization is an iterative testing process. Monitor component temperatures, test different fan configurations, and fine-tune your cooling setup based on your specific PC components and computing use cases. The investment in proper airflow optimization pays dividends in system performance, reliability, and component lifespan.
Key Takeaway: Focus on creating balanced positive air pressure, ensure proper case fan placement, and maintain your cooling system regularly. Proper PC cooling is essential for maintaining peak system performance and protecting your hardware investment.
